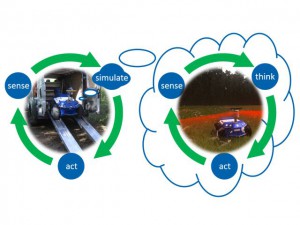
Life without satellites has become inconceivable in this day and age. Whether it is used for determination of position, to observe earth or for communication, the use of services made available by satellites has become a part of everyday life taken for granted. Without satellites, applications like vehicle global positioning systems, weather reports and satellite television are not possible on the quality and reliability level we have become accustomed to. With the increasing intensity with which space is used, the dangers to satellites are also on the rise. Especially space debris has become a massive ever-increasing problem in the past years, so that in the interim strong efforts aimed in the direction of sustainable space travel are being made. It is important to develop techniques and infrastructures for the maintenance and target-orientated waste disposal of satellites. Further considerations are the use of (re-) configurable satellite systems. A key building block to the attainment of these goals has to be robotics, a field which is being met with completely new challenges by the quest for sustainable space travel. MMI is meeting these challenges with the implementation and further development of different eRobotics techniques. A basic functionality mandatory for sustainable space travel is capturing the defective satellites with the help of free-flying space robots. Capturing and removing satellites is a complex maneuver, because every robotic movement, according to the Newton Law of “Action and Reaction”, leads to a counter-movement of the satellite. With optimized path planning, which leads to the seemingly “strange” movements of the robot, it can be guaranteed through use of eRobotics techniques that the satellite will also retain the desired orientation without the deployment of the thrusters. The dynamic decoupling between robotic arm and base minimizes the deviation from the initial position of the base. Optimized movement planning guides the gripper to the target point. The foundation for planning is an effective simulation on the basis of virtual test beds, incorporating different aspects of the task to be performed.